How is the Store organized ?
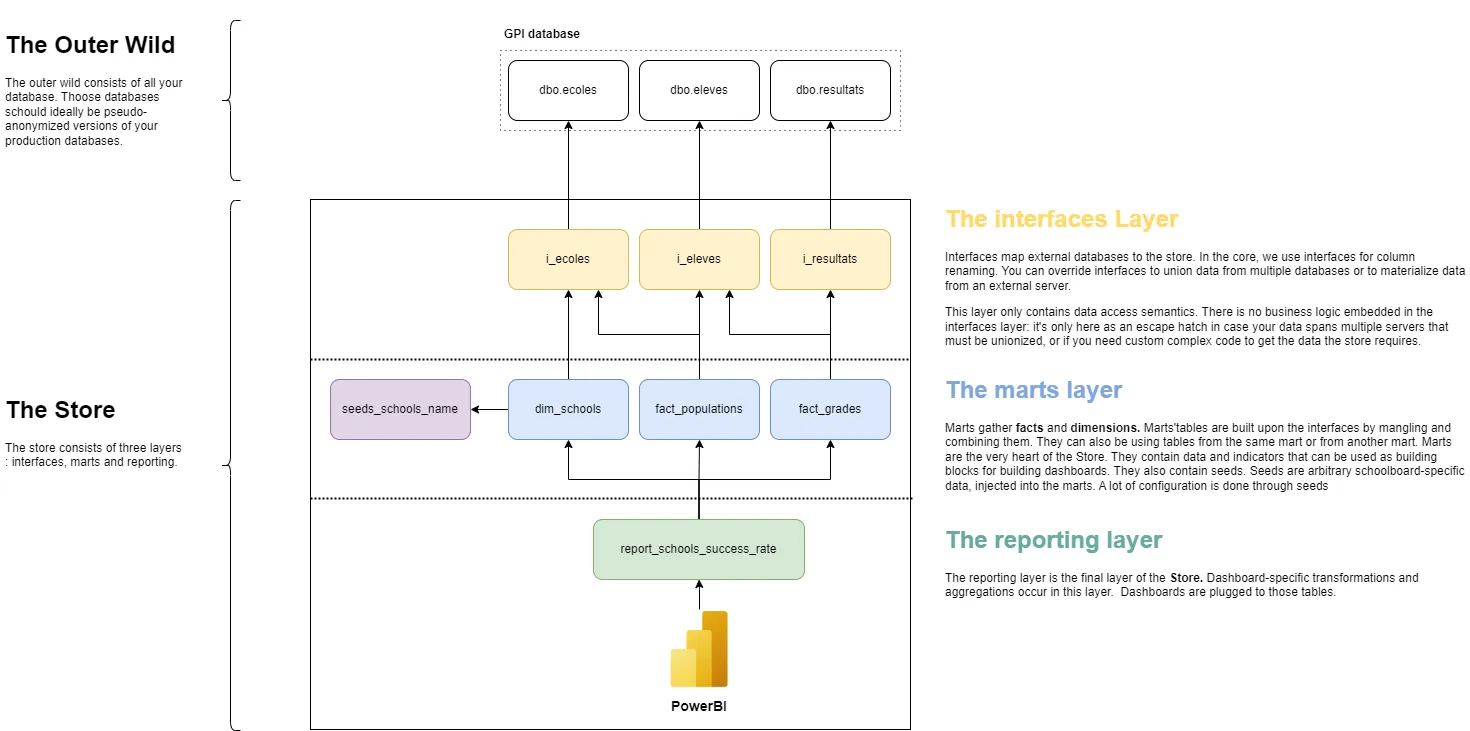
The 3-layers🧅
The interfaces layer
Interfaces map external databases (such as GPI, GRHPAIE, Bi_distribution) to the core_dashboards_store.
- When used in the
Core.dashboards_store, interfaces are almost always used to select and rename columns. - You can use interfaces in your
cssXX.dashboards_storeto :- Union data from multiple databases
- Materialize data from an external server
There schould never be any business logic in the interfaces layer. If you need to do some complex data transformation, you schould do it in the marts layer.
The marts layer
The bread-and-nutella of the core_dashboards_store.
Marts gather facts and dimensions. The store ships with two marts : education services and human ressources. More marts will be added in the future. Marts'tables are built upon the interfaces by mangling and combining them. They can also be using tables from the same mart or from another mart. They contain data and indicators that can be used as building blocks for building dashboards.
Usually, a mart table will be used by multiples dashboards.
Seeds, adapters and business rules
Not all the information we need can be pulled from the interfaces. Sometimes we need business rules to be feed into the core_dashboards_store. To do so, the store relays on two mechanisms : seeds and adapters.
- seeds : seeds are arbitrary data, injected into the marts. Is like a
csvfile automagically uploaded into the database prior to the ETL's run. A lot of configuration is done through seeds. As an example, thehuman_resourcesmarts use a seed to determine which employment codes schould be condidered asactive. As this is a schoolboard decision, thecorecan't provide you with this information by only using the database. You have to provide it yourself to the store, so it can be used in the ETL. It's mainly used for filtering and remapping. - adapters : adapters are arbitrary SQL code, injected into the marts. Sometimes, a seed is not flexible enough to handle schoolboard-scpecific business rule and you need to write some SQL code to do the job. Adapters are used to do so. As an example, the
education_servicesuse an adapter to determine which student is enrolled into an adapted program. As the business rule can greatly varies fromn one schoolboar to the other, it's not possible to provide a generic solution based on a pre-determined subset of columns.
The reporting layer
The reporting layers is where the magic happens. It's where the tables used by the dashboards are built.
Reporting layers contains the tables the dashboards are plugged onto. They are built upon the marts. They can also be using tables from the same reporting layer or from another reporting layer. The difference between the marts layer and the reporting layer is not a technical one but more of a semantical one : if the table is used by multiple dashboards, it's probably schould be in a mart. If it's only used by one dashboard, it schould belongs to the reporting layer.